 Belarusian
Statehood and Laws
Belarusian
Statehood and Laws 

VI-VIII
cc. Pre-Statehood
o
6th-7th
centuries: Penetration of Slavs into the territory of future Belarus, already
settled by Baltic tribes.
o 8th-9th
centuries: Massive settlements of East Slavic tribes (Kryvichans,
Drehovichans, and Radsimichans)
on the territory of Belarus and their assimilation of Balts (see the story of Yatviahs).
IX-XII
cc. Early Belarusian Principalities.- Polacak, Turau
o
862:
First mention of Polacak
- a capital of Polacak Principality - Belarusian
historical and spiritual beginning.
o 980:
First mention of the city Turau
- a capital of the powerful Turau principality.
o 1044-1066:
Erection in Polacak
of St. Sophia Cathedral to match similar buildings in Novgorod and Kiev, as
a symbol of independent power
XIII-XVI
cc. Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Samojitia and and Rus' - Belarusian
Renaissance
o 1240-1263:
Rule of Mindouh (Mindaugas), who consolidates east
Lithuanian and west Belarusian territories into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
with a capital in Navahradak
13th-16th centuries. Belarusian lands flourish in the heart of the Grand Duchy
of Lithuania, Samojitia and and
Rus'.
o 1529,
1566,1588 - Three editions of Statute - the Belarusian State Law Code - were
published among first European constitutions and Law Codes.
o 1581:
Establishment of the Tribunal of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Samojitia and and Rus' - the Supreme State Court.
1569 -
1772. Commonwealth of Poland. and Lithuania
o
1569:
A forced by Russian pressure from the East political union of the Grand Duchy
of Lithuania, Rus' and Samogitia
with Poland establishes the Commonwealth of Poland and Lithuania - Rzhecz Pospilita Polsko-Litewska.
o 1654-1667:
War of the Commonwealth with Russia; loss of Smalensk
to Muscovy. Close to half of Belarusians perish defending their lands from
Russian-Ukrainian invasion.
1772 -
1917. Part of Russian Empire. Kosciuszko and Kalinouski
Uprisings.
o
1772,
1793, 1795: Three partitions of the Polish Commonwealth among Russia, Prussia,
and Austria. All of Belarus is incorporated into the Russian Empire, with the exception of a small northwestern corner, taken by
Prussia. 1776: Most Belarusian cities and towns are deprived of their Magdeburg
Statutes of self-government. 1789: Onset of French Revolution. American Constitution
adopted.
o 1794:
Anti-Russian uprising led by Tadevush
Kasciushka (Thaddeus Kosciusko).
o 1863-1864:
Massive anti-tsarist uprising in Poland, Belarus, and Lithuania led in Belarus
by Kastus
Kalinouski
1918-1920
Belarusan Democratic Republic
o 1917: In March, the
Russian Revolution causes Tsar Nicholas II to abdicate. In November, Lenin's
Bolsheviks seize power. In December, the First All-Belarusan Congress in Minsk proclaims
a republican government in Belarus and is disbanded by Bolsheviks
o 1918:
On March 9, the Executive Committee of the Council of the First All-Belarusian
Congress
declares a Belarusan Democratic Republic.
1920-1939.
Byelorussian SSR. Partition of Belarus Between the USSR and Poland
o
1919-1921:
The Russo-Polish War results in the partitioning of Belarus between the
Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic and Poland
o 1921-1939
- Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR) is established with its capital
in Minsk. The short renaissance of Belarusian culture in 1920-1928 is choked by
Stalin's executions and mass deportations to Siberia of 1930-ies. Polish secret
police is prosecuting Belarusian political
organizations in Western Belarus occupied by Poles.
1939.
Re-Union of Western and Eastern Belarus
o
September
1939 - Poland is divided between Nazi Germany and USSR according to
Ribbentrop-Molotov secrect pact
o September 17, 1939 -
Red Army moves into Western Belarus and joins it with Eastern Belarus -
Byelorussian Socialist Republic.
o October
10, 1939 - Moscow transfers Belarusian cultural capital Vilnia
from Byelorussian SSR to Lithuanian SSR.
1941-1944.
Nazi Government of Belarus.
o
June
21, 1941 - July 13, 1944. Nazi occupation of Belarus. A collaborationist
government is created as a result of the II
All-Belarusian Congress.
1945-1991.
Post WWII Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
o
1945:
On April 25, delegates from Belarus and Ukraine are invited to the San
Francisco Conference. Recognized for their role in the war effort, both
countries become members of the United Nations
o 1944-1991.
Post-WWII Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR) is restored from ruins
with the help of other Republics. BSSR grows into
modern industrialized state.
1991-present.
Republic of Belarus - a Sovereign State
o
August
25, 1991. Belarus declares independence
o December 8, 1991 USSR seize to exist.
See more detailed Belarusian Historic
Timeline in our History Page.
Belarusian Constitution
This is a full text of the Constitution of the Republic of Belarus adopted on March 1, 1994. After 2 year in power Mr. Lukashenka has created a President post for himself in a new text of 1996 constitution by way of widely contested as rigged and un-democratic "National Referendum" of 1996. You can compare the texts of two constitutions here
Belarusian state anthem, symbol and flag
There is a confusion with the symbols since national referendum on May 14, 1995. By enormous majority (~77%) Belarusians readopted the old soviet flag of Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic and its symbol. I can only explain this outrageous act by the fact that Belarusan nationalist movement is following too extreme course for the most of Belarusians. Belarusians don't like extremes at all. Unfortunately the historical significance of the "Pahonia" symbol and white-red-white flag as Belarusian national symbols is now strongly overweighed by their political meaning as the symbols of extremist political party of national opposition. It is because of this strong political association that these symbols were rejected by majority of Belarusians on May 14, 1995. One other circumstance is that both white-red-white flag and "Pahonia" symbols were used by the collaborationist government established in Belarus by nazi during WWII occupation (read also a different opinion on this) and by Belarusian Democratic Republic established in Belarus during the WWI German occupation. This resulted in the negative attitude towards our historical symbols. There is very little knowledge of our true history in Belarus and of the historical value of "Pahonia" and white-red-white flag. The history of Belarus studied by the books of officially allowed Russian or Polish historians was very distorted. All of these authors, surprisingly including even soviet historians, were trying to hide to certain degree the fact of existence of Belarusian culture, our rich historical heritage, Belarusian people as a nation and, of course, our national symbols. Thus very few Belarusians, even with University degrees, know the true history of Belarus and its symbols.
 National
Anthem of Belarus
National
Anthem of Belarus
The anthem that was used before in a Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
sounds very ironic today when the national movement fights against the
President's course on dissolution of Belarus in Russia - " We are
Belarusians. We are searching our ways to happiness
together with our brothers in Russia..." etc. The old soviet melody still remains a national
anthem whereas the old words are rejected. The Janka Kupala poem "Young
Belarus" was selected as the text of a new Belarusian national anthem
whereas a melody is still not adopted. A complete melody of current Belarusian
anthem in wav format is saved as a zipped file (~2Mb) here.
 National Symbol of
Belarus
National Symbol of
Belarus
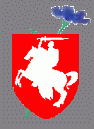
Our national symbol "Pahonia"
or in English -"Chase"- is the same for Belarus and Lithuania since
it comes from the days when Belarusians and Lithuanians were unified in one big
commonwealth of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Rus'. It shows a horseman with
a raised sword advancing on an enemy. You can read our special pages about the history of "Pahonia" symbol and its establishment as a
national emblem of Belarus. Find out more about "Pahonia"
symbol from the Lithuanian
server
 National
Flag of Belarus
National
Flag of Belarus
Correct me if I'm wrong but as for our national flag I've heard a following
story: During one of the battles with German knights (Grunwald) a white bandage
with a stripe of a blood stain across its center was used as a victorious
banner. Since that time our flag is white-red-white.
But this is a legend. Historically White-Red-white flag first appeared as the
national flag of Belarus in Belarusan Democratic
Republic (1918-1920.
The current official symbols of the Republic of Belarus
 and
and

∑ See also these information on Belarusian symbols and flags by Flags Of The World website
 Passport
of the citizen of the Republic of Belarus
Passport
of the citizen of the Republic of Belarus
Belarusian
passport is another symbol of Belarusian independence. Few of
them have been issued. I personally still have ex-USSR passport with Belarusian
"Pahonia" seal in it to symbolize that I am
Belarusian citizen. In 1991-1994 Belarusian passports were issued with "Pahonia" symbol. They were later replaced by the passports with Soviet "cabbage". Lukashenka
did not hesitated to spent our tax money to strip us
of our national symbols everywhere.
Belarusian Laws and Legal System
∑ History of Belarusian Law: Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were a great achievement of Belarusan Law. They were written during the 16th century and are among first European constitutions and Law codes. They have served later as an etalon to other European nations. The Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania are considered to be one of the main treasures (in addition to Lithuanian Metrics) of Belarusan, Lithuanian, and Polish culture.
∑ National Legal Internet Portal of the Republic of Belarus
∑ Constitution of the Republic of Belarus - original 1994 text and text with 1996 and 2004 ammendments,
∑ Short comparison of some paragraphs from the Constitution of Republic of Belarus (1994) and the Constitution (1996) by President of Belarus A. Lukashenka
∑ Belarusian Law page run by the U.S. House of Representatives Internet Law Library.
∑ Current violations of legal system, observed in Belarus - numerous human rights violations, persecution of NGOs and opposition, state sponsored dissapearings/executions of political opponents are TBD. Recently, a Parliamentary group of Deputies "Republic" went on hunger strike demanding strengthening election laws. The head of the group General Fralou has expressed his outrage with wide spread legal and judicial violations in Belarus by state judges and prosecutors, serving Lukashenka regime's hasty justice.
∑ Special legislation collection of Belarusian law for businessmen
- Civil law
- Legislation
on banks
- Monetary
legislation
- Standardization,
quality of products and services. Protection of consumers' rights
- Enterprises and
employers' activities
- Legislation
on agriculture and purchase of agricultural products
- Legislation
on mineral resources using the land
- Customs
legislation
- Criminal
legislation
- Legislation
on foreign economic activities
- Development
and advancement of legislation
- The
Governmental Policy towards Belarusian Language - interesting
developments concerning native language of the majority of Belarusians
Links related to Belarusian Statehood
- Belarusian
Constitution, Enactment Law and Declaration of
Independence presented in The International Constitutional Law (ICL)
Homepage at Cornell University.
Literature on the Belarusian Statehood
Ref. 1. "Belarusian Statehood. Reader and Bibliography", Ed.: Vitaut Kipel and Zora Kipel, Byelorussian Institute of Arts and Sciences, New York, 1988. Library of Congress Card #88-70081.
Ref. 2. Jan Zaprudnik, "Belarus: At a
Crossroads in History," Westview Press (now part of Harper
Collins),
1993, ISBN: 0-8133-1794-0 (pbk.)
You can order the book @ Harper Collinsr:
1-800-822-4090; fax: 1-800-242-7737; http://www.harpercollins.com/
Ref. 3. Zina Gimpelevich, "Two
Interviews with Vasil BykaŻ", In: Zapisy Vol. 23, published by Belarusian Institute of Arts
and Sciences, New York-1999.
 This file is a part of the Virtual Guide to Belarus - a collaborative
project of Belarusian scientists and
professionals abroad. VG brings you the most extensive compilation of
the information about Belarus on the Web.
This file is a part of the Virtual Guide to Belarus - a collaborative
project of Belarusian scientists and
professionals abroad. VG brings you the most extensive compilation of
the information about Belarus on the Web.
Please send your comments to the authors of
VG to Belarus
History | Statehood | Culture | Politics | Cities | Nature and Geography |
VG to
Belarus
Disclaimer